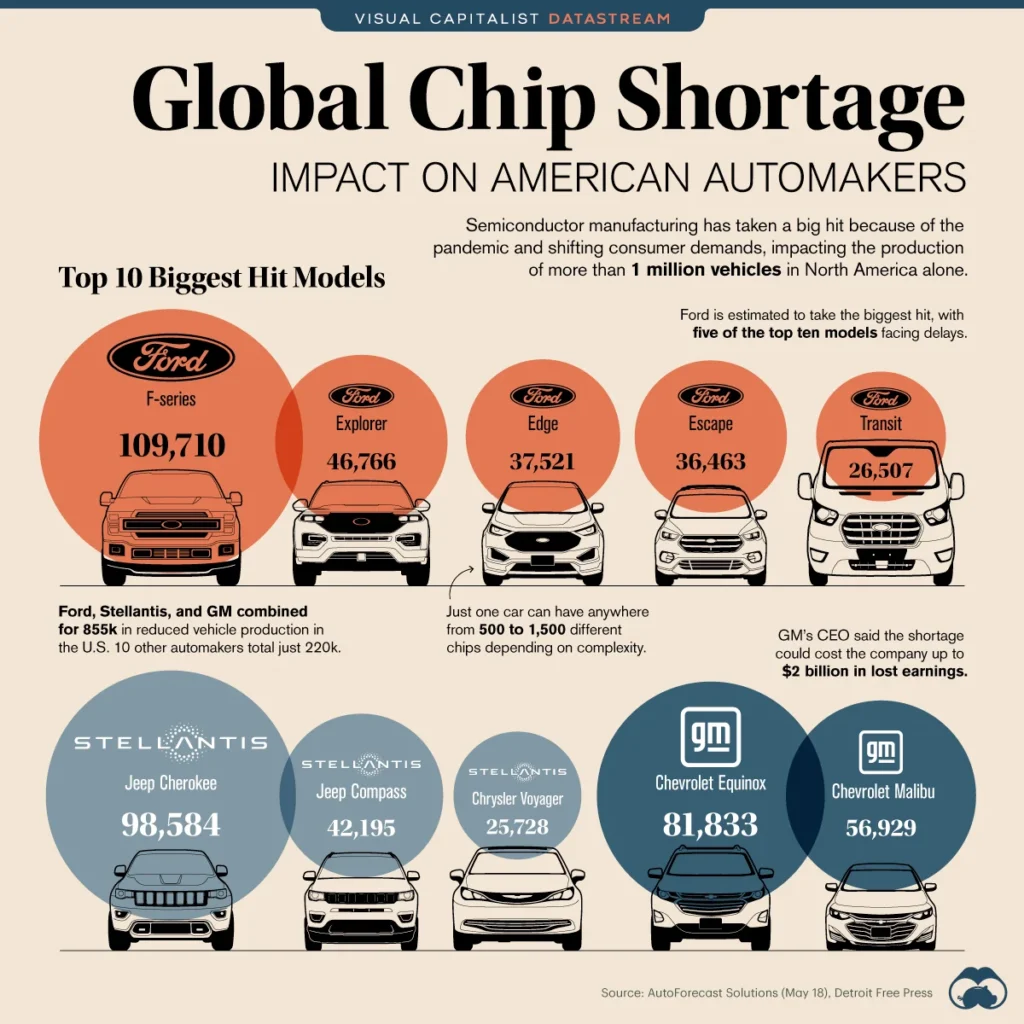
The global chip shortages have had a significant impact on the automobile industry. The shortage of semiconductor chips has disrupted the production of vehicles, leading to decreased supply and increased prices for consumers. Car manufacturers have been forced to scale back production and in some cases, temporarily halt production lines, resulting in delays for both new car deliveries and repairs. As a result, the chip shortages have caused a ripple effect throughout the entire automotive supply chain, affecting not only car manufacturers but also suppliers and dealers.
This issue has also sparked concerns about the future of electric and autonomous vehicles, as these technologies rely heavily on semiconductor chips. Furthermore, the chip shortages have highlighted the vulnerability of the global supply chain and raised questions about the industry’s dependence on a limited number of chip suppliers. As a result, car manufacturers are now exploring alternative options to secure a stable supply of chips, such as building strategic partnerships with chip manufacturers and investing in domestic chip production. The impact of the global chip shortages on the automobile industry is a complex and ongoing issue that will continue to shape the future of the automotive sector.
The Global Chip Shortage: A Crisis for the Automobile Industry
The global chip shortage has had a significant impact on the automobile industry, leading to production delays, reduced vehicle inventories, and increased prices for new cars. This shortage is the result of various factors, including the increased demand for consumer electronics, the disruption of supply chains due to the COVID-19 pandemic, and the complex manufacturing process of semiconductor chips. As a result, automakers are facing challenges in sourcing enough chips to keep up with production demands, leading to a ripple effect across the entire automotive sector.
Furthermore, the global chip shortage has forced many automakers to prioritize the production of high-margin vehicles, such as trucks and SUVs, over smaller, more affordable cars. This shift in production focus has impacted consumer choice and availability, as well as the overall profitability of car manufacturers. Additionally, the shortage has highlighted the vulnerability of the automotive industry to disruptions in the supply chain and has prompted discussions about the need for more resilient and flexible manufacturing strategies in the future.
Impact on Production and Inventory Levels
The chip shortage has resulted in production slowdowns and stoppages for many automobile manufacturers around the world. This has led to a decrease in the availability of new vehicles, as well as a reduction in the variety of models and options offered to consumers. As a result, car dealerships are facing challenges in maintaining adequate inventory levels to meet customer demand, leading to longer wait times and higher prices for new cars.
Furthermore, the production disruptions caused by the chip shortage have also impacted the supply of used vehicles, as fewer new cars being produced means fewer trade-ins and lease returns entering the market. This has contributed to a tightening of the overall vehicle supply, leading to increased competition among buyers and higher prices for pre-owned vehicles. The impact of the chip shortage on production and inventory levels is expected to continue for the foreseeable future, with automakers and suppliers working to address the underlying issues.
Supply Chain Vulnerabilities and Resilience Efforts
The global chip shortage has highlighted the vulnerabilities in the automotive industry’s supply chain, particularly in its reliance on a limited number of semiconductor suppliers and the complex logistics of chip production. As a result, there is a growing focus on building more resilient and diversified supply chains to mitigate the impact of future disruptions. This includes efforts to increase domestic chip production, establish strategic stockpiles of critical components, and forge stronger partnerships with semiconductor suppliers.
Additionally, automakers are exploring alternative technologies and designs that require fewer chips or can use different types of chips that are more readily available. This includes re-evaluating the use of chips in non-critical systems and implementing software and hardware optimizations to make more efficient use of available semiconductor resources. These resilience efforts aim to reduce the industry’s susceptibility to future chip shortages and ensure a more stable and sustainable supply chain for the production of vehicles.
Impact on Innovation and Technological Advancements
The chip shortage has also had implications for the development and integration of advanced technologies in the automotive industry. Many new vehicles rely on semiconductor chips for a wide range of functions, including infotainment systems, advanced driver-assistance systems (ADAS), and electrification components. The shortage has led to delays in the rollout of new models and features, as well as challenges in meeting regulatory requirements for safety and emissions standards.
Furthermore, the prioritization of high-margin vehicles over smaller, more fuel-efficient models has impacted the industry’s efforts to transition towards electric and hybrid vehicles. The shortage of chips has hindered the production of electric vehicle components, such as battery management systems and powertrain controls, leading to delays in the expansion of electric vehicle offerings from many automakers. As a result, the chip shortage has slowed down the pace of innovation and technological advancements in the automotive sector, affecting the industry’s ability to meet evolving consumer demands and environmental targets.
Financial Implications for Automakers and Suppliers
The global chip shortage has had significant financial implications for both automakers and their suppliers. Production slowdowns and stoppages have resulted in revenue losses and increased manufacturing costs, as well as the need to invest in alternative solutions to address the chip shortage. This has impacted the profitability and financial performance of many companies in the automotive supply chain, leading to challenges in meeting investor expectations and maintaining stable operations.
Additionally, the chip shortage has prompted automakers to re-evaluate their procurement strategies and supply chain management practices to minimize future risks. This includes revisiting long-term contracts with semiconductor suppliers, diversifying sourcing options, and building strategic reserves of critical components. These measures come with associated costs and complexities, further impacting the financial outlook for the industry as a whole. As a result, the chip shortage has underscored the need for greater financial resilience and risk management in the automotive sector.
Consumer Impact: Higher Prices and Longer Wait Times
For consumers, the global chip shortage has translated into higher prices and longer wait times for new vehicles. As automakers grapple with production challenges, they have been forced to increase prices to offset the impact of the chip shortage on their operations. This has made new cars less affordable for many prospective buyers, leading to a shift in consumer preferences towards the used car market or delaying their vehicle purchases altogether.
Furthermore, the limited availability of new vehicles has led to longer wait times and reduced bargaining power for consumers, as dealerships struggle to fulfill orders and maintain adequate inventory levels. This has created a more competitive and challenging landscape for car buyers, who may face increased pressure to make purchasing decisions quickly and may have limited options in terms of vehicle models and features. The consumer impact of the chip shortage is expected to persist until production levels normalize and supply chain issues are resolved.
Government and Industry Response to the Chip Shortage
The global chip shortage has prompted governments and industry organizations to take action to address the underlying issues and mitigate the impact on the automotive sector. This includes initiatives to support domestic semiconductor manufacturing, invest in research and development for advanced chip technologies, and establish partnerships between governments, automakers, and semiconductor suppliers to secure the supply of critical components.
Furthermore, there is a growing recognition of the need to improve forecasting and demand planning practices to better anticipate and respond to future supply chain disruptions. This includes the development of early warning systems, the sharing of best practices among industry participants, and the implementation of more flexible production processes that can adapt to changes in supply and demand dynamics. The government and industry response to the chip shortage aims to build a more resilient and sustainable foundation for the automotive industry’s future growth and innovation.
Long-Term Implications and the Future of the Automotive Industry
The global chip shortage has raised important questions about the long-term implications for the automotive industry and its future trajectory. This includes considerations about the industry’s reliance on advanced technologies, the resilience of its supply chain, and the balance between innovation and risk management. The shortage has also underscored the need for greater collaboration and coordination among industry stakeholders, including automakers, suppliers, and governments, to address systemic challenges and build a more sustainable and adaptable automotive ecosystem.
Furthermore, the chip shortage has accelerated discussions about the role of electrification, autonomous driving, and connected technologies in shaping the future of mobility. As the industry navigates through the challenges posed by the shortage, there is an opportunity to re-evaluate priorities, invest in new capabilities, and chart a course towards a more resilient, efficient, and innovative automotive industry. The long-term implications of the chip shortage are likely to influence the strategic decisions and investments made by industry participants as they prepare for a more dynamic and technology-driven future.
| Issue | Impact |
|---|---|
| Production Disruptions | Automakers are facing production halts and slowdowns due to the shortage of semiconductor chips, leading to decreased vehicle output. |
| Increased Costs | Automobile companies are experiencing higher costs as they compete for a limited supply of chips, impacting their profitability. |
| Delayed Innovation | The shortage is hindering the development of new vehicle features and technologies that rely on advanced semiconductor components. |
| Consumer Impact | Consumers may face limited vehicle options, increased prices, and longer wait times due to the chip shortages affecting the industry. |
The global chip shortages have significantly disrupted the automobile industry, leading to production delays, increased costs, hindered innovation, and potential impacts on consumers. As semiconductor chips continue to be a critical component in modern vehicles, addressing the shortage has become a priority for automakers and the broader supply chain.