As we stand on the brink of a technological revolution, the question of “Autonomous Vehicles: Are We Ready For Full Automation?” has become increasingly pertinent. With advancements in artificial intelligence, machine learning, and sensor technology, self-driving cars are no longer a distant dream but a rapidly approaching reality. This article delves into the current state of autonomous vehicles, examining the potential benefits and challenges that come with full automation. Are we prepared to embrace this change, or are there hurdles yet to overcome?
In the following sections, we will explore the various levels of automation in vehicles, from basic driver assistance systems to fully autonomous driving capabilities. You will learn about the technological innovations that are paving the way for self-driving cars, as well as the regulatory and ethical considerations that must be addressed. Additionally, we will discuss the impact of autonomous vehicles on society, including safety, traffic management, and environmental implications.
Join us as we navigate through the complexities of autonomous vehicles and their journey towards full automation. By the end of this article, you will have a comprehensive understanding of the current landscape and future prospects of self-driving technology. So buckle up and get ready to explore whether we are truly ready for the age of autonomous vehicles!
The Current State of Autonomous Vehicle Technology
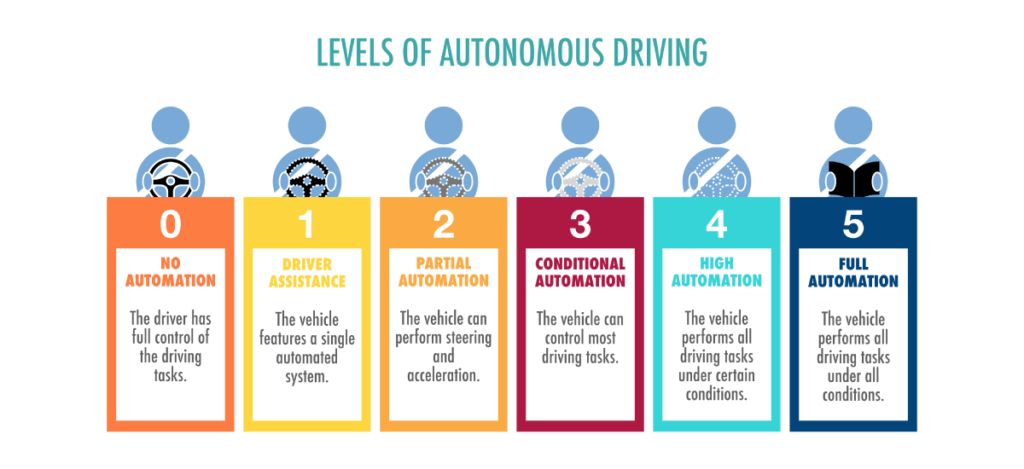
The development of autonomous vehicle technology has made significant strides in recent years. Major automotive manufacturers and tech companies are investing heavily in research and development to create vehicles that can operate without human intervention. Current systems, such as Level 2 and Level 3 automation, allow for features like adaptive cruise control and lane-keeping assistance, but they still require human oversight. As we move towards Level 4 and Level 5 automation, the technology must overcome various challenges, including complex urban environments and unpredictable human behavior.
Moreover, advancements in artificial intelligence, machine learning, and sensor technology are crucial for achieving full automation. These technologies enable vehicles to perceive their surroundings, make decisions, and navigate safely. However, the integration of these systems into a cohesive and reliable platform remains a significant hurdle. The question arises: are we truly ready for the leap to fully autonomous vehicles, or do we still have a long way to go?
Legal and Regulatory Challenges
The legal landscape surrounding autonomous vehicles is still evolving. Governments worldwide are grappling with how to regulate this new technology, which raises questions about liability, insurance, and safety standards. In the event of an accident involving an autonomous vehicle, determining fault can be complex. Is it the manufacturer, the software developer, or the vehicle owner who is responsible? These legal ambiguities create uncertainty that can hinder the widespread adoption of autonomous vehicles.
Additionally, regulatory bodies must establish clear guidelines for testing and deploying autonomous vehicles on public roads. This includes setting safety standards, conducting rigorous testing, and ensuring that vehicles can communicate effectively with other road users. As the technology continues to develop, it is essential for lawmakers to keep pace and create a framework that fosters innovation while ensuring public safety.
Public Perception and Acceptance
Public perception plays a crucial role in the acceptance of autonomous vehicles. While many people are excited about the potential benefits, such as reduced traffic accidents and increased mobility for the elderly and disabled, there are also significant concerns. Issues such as safety, privacy, and the potential loss of jobs in the transportation sector contribute to skepticism. Surveys indicate that a substantial portion of the population is hesitant to trust fully autonomous vehicles, often citing fears of technology failure or hacking.
To address these concerns, manufacturers and policymakers must engage in transparent communication and education efforts. Demonstrating the safety and reliability of autonomous vehicles through pilot programs and real-world data can help build trust. Additionally, addressing ethical considerations, such as decision-making in unavoidable accident scenarios, is vital for gaining public acceptance.
Economic Implications of Full Automation
The economic impact of fully autonomous vehicles could be profound. On one hand, the technology promises to reduce costs associated with accidents, traffic congestion, and fuel consumption. On the other hand, it poses challenges for industries reliant on human drivers, such as trucking and taxi services. The transition to automation may lead to job displacement for millions of workers, necessitating retraining and support programs to help them adapt to new roles in a changing economy.
Moreover, the rise of autonomous vehicles could reshape urban planning and infrastructure. With fewer cars on the road, cities may need to rethink their transportation systems, potentially leading to reduced parking needs and more pedestrian-friendly environments. Understanding these economic implications is crucial for stakeholders as they navigate the transition to a more automated future.
Safety and Ethical Considerations
Safety is paramount when discussing autonomous vehicles. While proponents argue that automation can reduce human error, which is responsible for the majority of traffic accidents, the technology is not without its risks. Incidents involving autonomous vehicles, such as the high-profile Uber self-driving car fatality, highlight the need for rigorous safety protocols and testing before widespread deployment.
Ethical considerations also come into play, particularly regarding decision-making in critical situations. For instance, how should an autonomous vehicle prioritize the safety of its passengers versus pedestrians in an unavoidable accident scenario? These ethical dilemmas require careful thought and public discourse to ensure that the deployment of autonomous vehicles aligns with societal values.
The Future of Transportation: Integration with Smart Cities
The future of transportation is likely to be intertwined with the development of smart cities. Autonomous vehicles can play a pivotal role in creating more efficient and sustainable urban environments. By integrating with smart infrastructure, such as traffic management systems and connected devices, autonomous vehicles can optimize traffic flow, reduce
| Aspect | Description |
|---|---|
| Definition | Autonomous vehicles (AVs) are capable of sensing their environment and operating without human intervention. |
| Levels of Automation | There are six levels of automation, ranging from Level 0 (no automation) to Level 5 (full automation). |
| Current State | Most AVs on the market today are at Level 2 or Level 3, requiring human oversight. |
| Technological Challenges | Challenges include sensor reliability, software algorithms, and the ability to handle complex driving scenarios. |
| Regulatory Issues | Governments are still developing regulations and standards for the safe deployment of AVs. |
| Public Perception | Public trust in AV technology is crucial; many people are still skeptical about safety and reliability. |
| Ethical Considerations | AVs raise ethical questions regarding decision-making in accident scenarios and liability issues. |
| Infrastructure Readiness | Current road infrastructure may need upgrades to support fully autonomous vehicles. |
| Future Outlook | Experts predict gradual adoption of AVs, with full automation potentially becoming mainstream in the next few decades. |