As the automotive industry evolves, the debate between electric and hybrid cars has become increasingly relevant. With growing concerns about climate change and the need for sustainable transportation, many consumers are left wondering: Electric Vs. Hybrid Cars: Which One To Choose? Both options offer unique advantages and challenges, making it essential to understand their differences before making a decision. In this article, we will delve into the key features of electric and hybrid vehicles, helping you navigate this important choice.
In the following sections, we will explore the environmental benefits of electric cars compared to hybrids, including their impact on reducing carbon emissions. Additionally, we will discuss the cost implications of both vehicle types, from initial purchase prices to long-term savings on fuel and maintenance. Furthermore, we will examine the driving experience, charging infrastructure, and the latest technological advancements that are shaping the future of these vehicles.
Whether you are an eco-conscious driver or simply looking for a more efficient way to commute, understanding the nuances of electric and hybrid cars is crucial. By the end of this article, you will be equipped with the knowledge needed to make an informed decision that aligns with your lifestyle and values. So, buckle up and join us as we explore the exciting world of electric and hybrid vehicles!
Understanding the Basics of Electric and Hybrid Cars
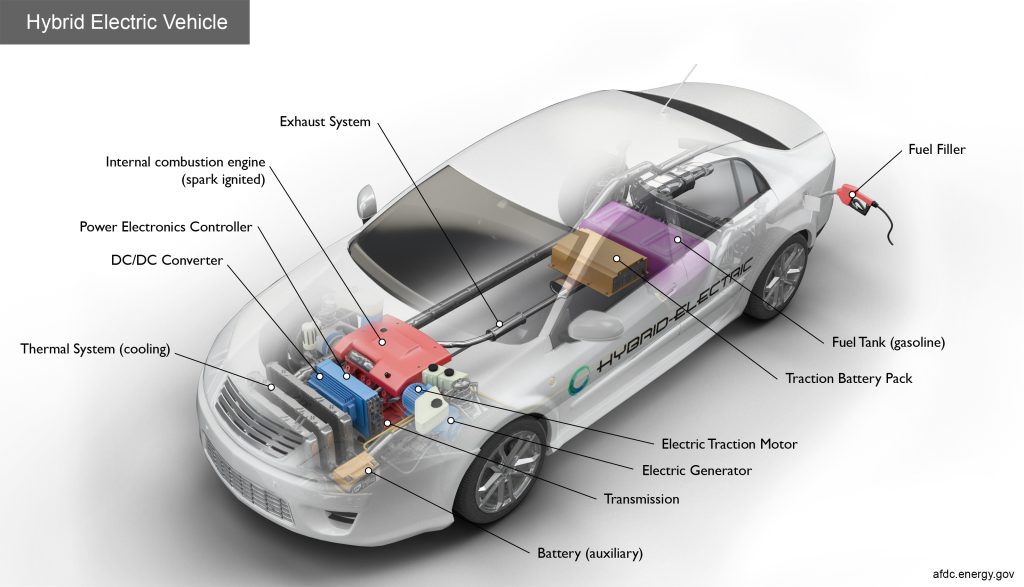
Electric cars (EVs) are powered entirely by electricity, using large battery packs to store energy. They produce zero tailpipe emissions, making them an environmentally friendly option. On the other hand, hybrid cars combine a traditional internal combustion engine with an electric motor, allowing for improved fuel efficiency and reduced emissions compared to conventional vehicles. Understanding these fundamental differences is crucial for potential buyers.
When considering the choice between electric and hybrid cars, it’s essential to evaluate your driving habits. Electric vehicles are ideal for those who primarily drive short distances and have access to charging stations. In contrast, hybrids offer greater flexibility for longer trips, as they can switch to gasoline when the battery is depleted. This makes hybrids a practical choice for individuals who may not have reliable access to charging infrastructure.
Cost of Ownership: Initial Investment and Long-Term Savings
The initial cost of electric vehicles can be higher than that of hybrids or traditional cars, primarily due to the expensive battery technology. However, many governments offer incentives and tax credits for EV purchases, which can significantly reduce the upfront cost. Additionally, electric cars typically have lower operating costs, as electricity is generally cheaper than gasoline, and they require less maintenance due to fewer moving parts.
In contrast, hybrid vehicles often have a lower initial purchase price compared to electric cars, but they may not offer the same level of long-term savings. While hybrids do benefit from improved fuel efficiency, they still rely on gasoline, which can fluctuate in price. Over time, the total cost of ownership for an electric vehicle may be more favorable, especially when considering factors like fuel savings and maintenance costs.
Environmental Impact: Emissions and Sustainability
One of the most significant advantages of electric vehicles is their minimal environmental impact. Since they produce no tailpipe emissions, EVs contribute to cleaner air and reduced greenhouse gas emissions. Additionally, as the electricity grid becomes greener with more renewable energy sources, the overall carbon footprint of electric cars continues to decrease.
Hybrid cars, while more efficient than traditional vehicles, still emit pollutants due to their reliance on gasoline. However, they do offer a transitional solution for those looking to reduce their carbon footprint without fully committing to an electric vehicle. It’s essential to consider the environmental implications of your choice, as both options contribute to sustainability in different ways.
Charging Infrastructure and Convenience
Charging infrastructure is a critical factor when deciding between electric and hybrid cars. Electric vehicles require access to charging stations, which can be a concern for potential buyers, especially in areas with limited infrastructure. However, the number of charging stations is rapidly increasing, and many EV owners choose to install home charging units for added convenience.
Hybrids, on the other hand, do not require charging stations, as they can operate solely on gasoline. This makes them a more convenient option for those who frequently travel long distances or live in areas where charging infrastructure is lacking. Ultimately, the choice may come down to your lifestyle and how often you can access charging facilities.
Performance and Driving Experience
When it comes to performance, electric vehicles often provide a smoother and quieter ride due to their instant torque and lack of engine noise. Many EVs are designed for high performance, offering quick acceleration and responsive handling. This can enhance the overall driving experience, making electric cars an appealing choice for those who prioritize performance.
Hybrid vehicles, while generally efficient, may not deliver the same level of performance as their electric counterparts. However, they do offer a balance between power and efficiency, making them suitable for a wide range of driving conditions. Ultimately, the choice between electric and hybrid cars will depend on your personal preferences and driving style.
| Feature | Electric Cars | Hybrid Cars |
|---|---|---|
| Power Source | Powered entirely by electricity stored in batteries. | Combines a gasoline engine with an electric motor. |
| Fuel Efficiency | Highly efficient, zero fuel consumption when driving on electric power. | More fuel-efficient than traditional cars, but still uses gasoline. |
| Emissions | Zero tailpipe emissions, environmentally friendly. | Lower emissions than conventional vehicles, but still produces some. |
| Range | Limited range depending on battery capacity, typically 100-300 miles. | Extended range due to gasoline engine, often over 600 miles. |
| Charging | Requires charging stations; home charging is common. | Can be fueled at gas stations and charged at electric stations. |
| Maintenance | Lower maintenance costs due to fewer moving parts. | More complex due to dual power sources, potentially higher maintenance costs. |
| Initial Cost | Generally higher upfront cost, but incentives may apply. | Usually lower than electric cars, but varies by model. |
| Driving Experience | Quiet and smooth driving experience with instant torque. | Can switch between electric and gasoline, offering versatility. |
Conclusion
Choosing between electric and hybrid cars depends on individual needs and preferences. Electric cars are ideal for those seeking an eco-friendly option with lower operating costs, while hybrid cars offer flexibility and extended range for longer trips. Consider your driving habits, budget, and environmental impact when making a decision.